Cost analysis is a useful tool to make your API more secure. With Hot Chocolate, static cost analysis is built in, and is based on the draft IBM Cost Analysis specification.
Directives
Cost directive
The purpose of the @cost directive is to define a weight for GraphQL types, fields, and arguments. Static analysis can use these weights when calculating the overall cost of a query or response.
The weight argument defines what value to add to the overall cost for every
appearance, or possible appearance, of a type, field, argument, etc.
The @cost directive can be applied to argument definitions, enums, field definitions, input field definitions, object types, and scalars.
List Size directive
The purpose of the @listSize directive is to either inform the static analysis about the size of returned lists (if that information is statically available), or to point the analysis to where to find that information.
- The
assumedSizeargument can be used to statically define the maximum length of a list returned by a field. - The
slicingArgumentsargument can be used to define which of the field's arguments with numeric type are slicing arguments, so that their value determines the size of the list returned by that field. It may specify a list of multiple slicing arguments. - The
sizedFieldsargument can be used to define that the value of theassumedSizeargument or of a slicing argument does not affect the size of a list returned by a field itself, but that of a list returned by one of its sub-fields. - The
requireOneSlicingArgumentargument can be used to inform the static analysis that it should expect that exactly one of the defined slicing arguments is present in a query. If that is not the case (i.e., if none or multiple slicing arguments are present), the static analysis will throw an error.
The @listSize directive can only be applied to field definitions.
Defaults
By default, Hot Chocolate will apply a cost weight of 10 to async resolvers, 1 to composite types, and 0 to scalar fields.
Filtering and sorting field arguments and operations also have default cost weights, as shown in their respective Options section below.
Finally, resolvers using pagination will have list size settings applied automatically:
books(first: Int, after: String, last: Int, before: String): BooksConnection @listSize( assumedSize: 50 slicingArguments: ["first", "last"] sizedFields: ["edges", "nodes"] ) @cost(weight: "10")
Applying a cost weight
When using an implementation-first approach, apply the Cost attribute to the query resolver.
[QueryType]public static class Query{ [Cost(100)] public static Book GetBook() => new("C# in depth.", new Author("Jon Skeet"));}
Applying list size settings
When using an implementation-first approach, apply the ListSize attribute to a query resolver returning a list of items.
[QueryType]public static class Query{ [ListSize( AssumedSize = 100, SlicingArguments = ["first", "last"], SizedFields = ["edges", "nodes"], RequireOneSlicingArgument = false)] public static IEnumerable<Book> GetBooks() => [new("C# in depth.", new Author("Jon Skeet"))];}
Cost metrics
Cost metrics include two properties, FieldCost and TypeCost:
FieldCostrepresents the execution impact on the server.TypeCostrepresents the data impact on the server (instantiated objects).
Accessing cost metrics
To access the cost metrics via the IResolverContext or IMiddlewareContext, use the context data key WellKnownContextData.CostMetrics:
public static Book GetBook(IResolverContext resolverContext){ const string key = WellKnownContextData.CostMetrics; var costMetrics = (CostMetrics)resolverContext.ContextData[key]!;
double fieldCost = costMetrics.FieldCost; double typeCost = costMetrics.TypeCost;
// ...}
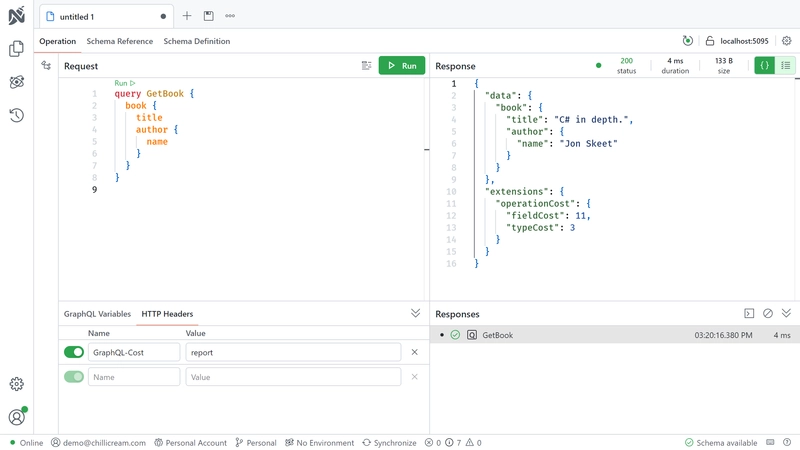
Reporting cost metrics
To output the cost metrics, set an HTTP header named GraphQL-Cost with one of the following values:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
report | The request is executed, and the costs are reported in the response. |
validate | The costs are reported in the response, without executing the request. |
Note: When using
validate, Nitro will currently not display the response in theResponsepane. Until this is fixed, you can inspect the response body in the request log.
Cost calculation examples
Field cost
query { book { # 10 (async resolver) title # 0 (scalar) author { # 1 (composite type) name # 0 (scalar) } }}
# Field cost: 11
Type cost
query { # 1 Query book { # 1 Book title author { # 1 Author name } }}
# Type cost: 3
Options
Cost options
Options for cost analysis.
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| MaxFieldCost | Gets or sets the maximum allowed field cost. | 1_000 |
| MaxTypeCost | Gets or sets the maximum allowed type cost. | 1_000 |
| EnforceCostLimits | Defines if the analyzer shall enforce cost limits. | true |
| ApplyCostDefaults | Defines if cost defaults shall be applied to the schema. | true |
| DefaultResolverCost | Gets or sets the default cost for an async resolver pipeline. | 10.0 |
Modifying cost options:
builder.Services .AddGraphQLServer() .ModifyCostOptions(options => { options.MaxFieldCost = 1_000; options.MaxTypeCost = 1_000; options.EnforceCostLimits = true; options.ApplyCostDefaults = true; options.DefaultResolverCost = 10.0; });
Filtering cost options
Represents the cost options for filtering.
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| DefaultFilterArgumentCost | Gets or sets the default cost for a filter argument. | 10.0 |
| DefaultFilterOperationCost | Gets or sets the default cost for a filter operation. | 10.0 |
| DefaultExpensiveFilterOperationCost | Gets or sets the default cost for an expensive filter argument. | 20.0 |
| VariableMultiplier | Gets or sets a multiplier when a variable is used for the filter argument. | 5 |
Modifying filtering cost options:
builder.Services .AddGraphQLServer() .ModifyCostOptions(options => { options.Filtering.DefaultFilterArgumentCost = 10.0; options.Filtering.DefaultFilterOperationCost = 10.0; options.Filtering.DefaultExpensiveFilterOperationCost = 20.0; options.Filtering.VariableMultiplier = 5; });
Sorting cost options
Represents the cost options for sorting.
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| DefaultSortArgumentCost | Gets or sets the default cost for a sort argument. | 10.0 |
| DefaultSortOperationCost | Gets or sets the default cost for a sort operation. | 10.0 |
| VariableMultiplier | Gets or sets multiplier when a variable is used for the sort argument. | 5 |
Modifying sorting cost options:
builder.Services .AddGraphQLServer() .ModifyCostOptions(options => { options.Sorting.DefaultSortArgumentCost = 10.0; options.Sorting.DefaultSortOperationCost = 10.0; options.Sorting.VariableMultiplier = 5; });
Disabling cost limit enforcement
While we generally don't recommended disabling the enforcement of cost limits, you may wish to do so if you're using other methods to restrict operation complexity. If that's the case, simply set the EnforceCostLimits option to false:
builder.Services .AddGraphQLServer() .ModifyCostOptions(o => o.EnforceCostLimits = false)