Nitro includes Open Telemetry logging, allowing seamless log collection and analysis directly within the app. This documentation provides guidance on setting up and utilizing logging features in Nitro for enhanced monitoring, debugging, and performance analysis of your APIs.
API Logs
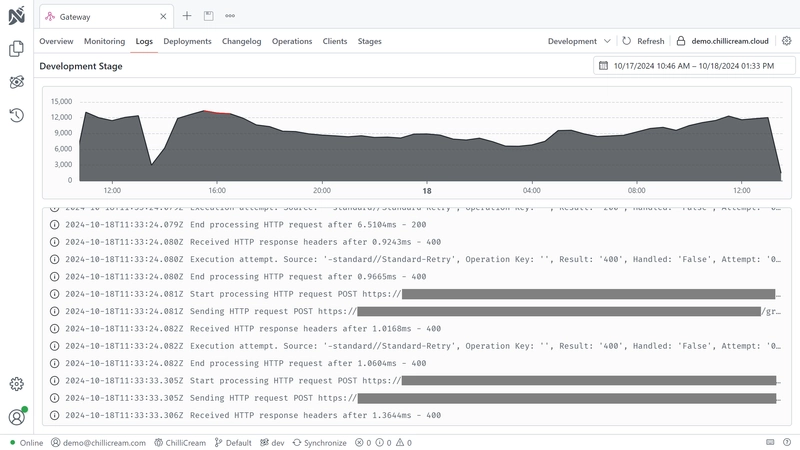 Each API in Nitro features a Logs tab, providing a centralized interface for viewing and managing logs associated with your API.
This unified log view offers insights into your system’s activities, enabling you to monitor and troubleshoot in real-time.
Each API in Nitro features a Logs tab, providing a centralized interface for viewing and managing logs associated with your API.
This unified log view offers insights into your system’s activities, enabling you to monitor and troubleshoot in real-time.
Detailed Log Inspection
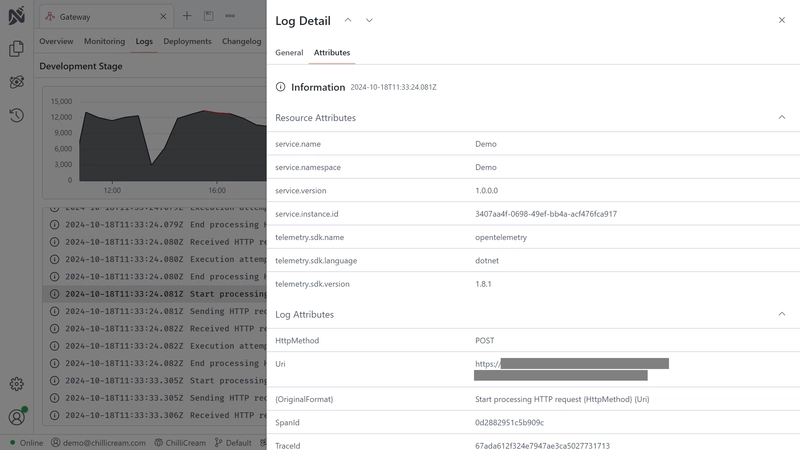
Within the Logs tab, individual log entries can be expanded to reveal additional details such as timestamps, log levels, and message content.
Trace Logs
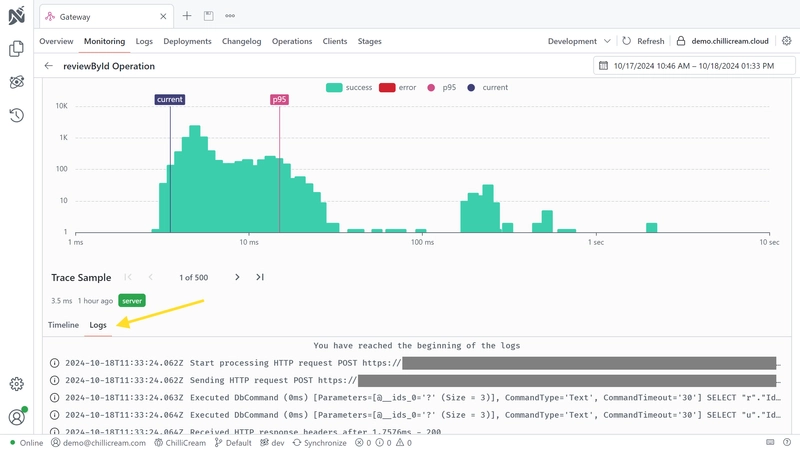
Logs can also be inspected within individual traces, providing detailed insights into the correlation between specific traces and their corresponding logs.
Log Retention
Log retention in Nitro is configured as follows:
- Shared Clusters: Logs are retained for 1 day to allow for recent log review.
- Dedicated Clusters: Dynamic log retention times can be configured to meet specific needs, offering flexibility in log management.
Connect your service
All the logging is done on a per API basis. An api represents one of your deployments. To monitor you services you need to create an API in Nitro. The api needs to be from type "Api Service" or "Api Gateway".
To install the Nitro services, run the following commands in your project's root directory:
dotnet add package ChilliCream.Nitrodotnet add package OpenTelemetry.Extensions.Hostingdotnet add package OpenTelemetry.Instrumentation.AspNetCore
After installing the package, you need to configure the services in your startup class. Below is a sample implementation in C#:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services){ services .AddGraphQLServer() .AddQueryType<Query>() .AddNitro(x => { x.ApiKey = "<<your-api-key>>"; x.ApiId = "QXBpCmc5NGYwZTIzNDZhZjQ0NjBmYTljNDNhZDA2ZmRkZDA2Ng=="; x.Stage = "dev"; }) .AddInstrumentation();
services .AddLogging(x => x .AddNitroExporter() .AddOpenTelemetry(options => { options.IncludeFormattedMessage = true; options.IncludeScopes = true; }));}
Tip: Using Environment Variables
Alternatively, you can set the required values using environment variables. This method allows you to call
AddNitrowithout explicitly passing parameters.
NITRO_API_KEYmaps toApiKeyNITRO_API_IDmaps toApiIdNITRO_STAGEmaps toStageC#public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services){services.AddGraphQLServer().AddQueryType<Query>().AddNitro().AddInstrumentation(); // Enable the graphql telemetryservices.AddLogging(x => x.AddNitroExporter().AddOpenTelemetry(options =>{options.IncludeFormattedMessage = true;options.IncludeScopes = true;}));}In this setup, the API key, ID, and stage are set through environment variables.
Full Example
For a complete implementation example, visit the example repository.